Amoxicillin clavulanate is a broad spectrum antibiotic which is used frequently in New Zealand
general practice. The proportion of people using amoxicillin clavulanate has steadily increased over
the last three years in comparison to other penicillins.
This report will discuss the use of amoxicillin clavulanate in general practice using data from the
Ministry of Health National Collections for all amoxicillin clavulanate dispensed in 2012.
In this article 
View / Download pdf
version of this article
Reserving the use of amoxicillin clavulanate
Amoxicillin clavulanate is an important and effective medicine but its use must be reserved for specific indications
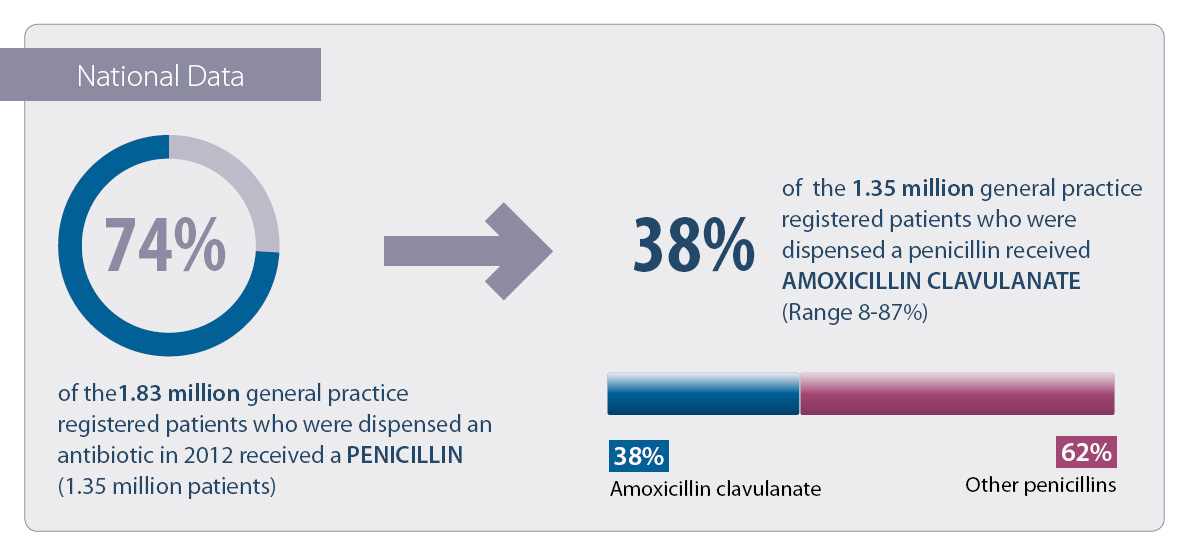
in order to reduce the rate of antimicrobial resistant infections. Amoxicillin clavulanate accounted for 18% of all national
antibiotic dispensings in 2012. While amoxicillin clavulanate and other broad spectrum antibiotics (quinolones and cephalosporins)
are effective, they are best avoided when other more narrow-spectrum antibiotics could be used, because they contribute
to increasing antimicrobial resistance e.g. MRSA.1
Indications for amoxicillin clavulanate2
Amoxicillin clavulanate is best reserved for the few indications where it is necessary so that it remains an effective
antibiotic when needed and the adverse effects associated with the use of broad spectrum antibiotics are avoided. First-line
indications include; bites (mammalian-including human), diabetic foot infections and acute pyelonephritis. Please refer
to the bpacnz 2013 antibiotic guideline for further information.
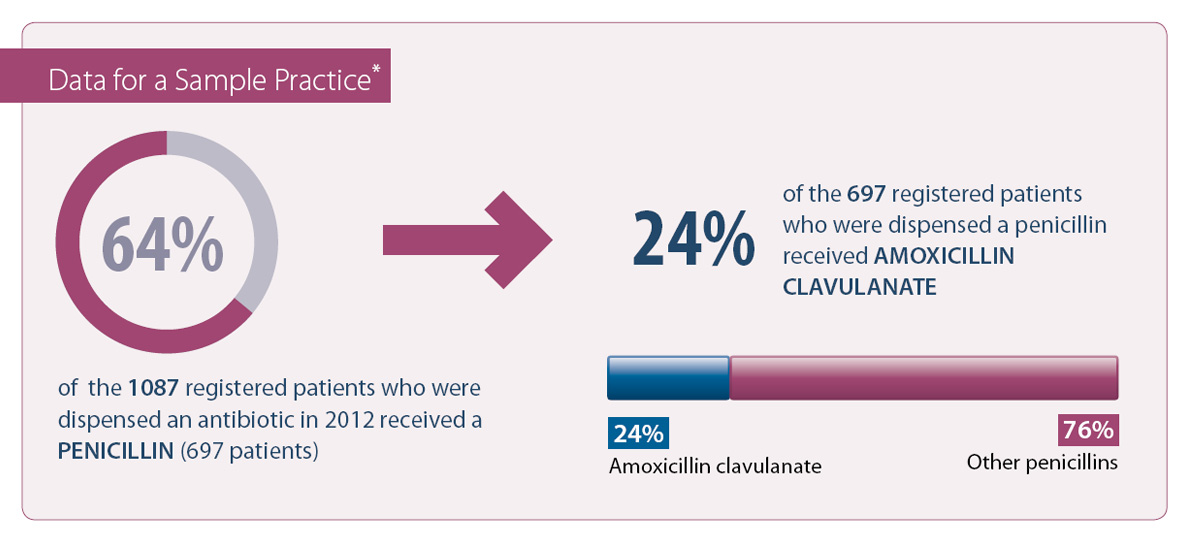
* These data include prescribing by any New Zealand health provider including those who do not work in your practice.
For individual annual report data on amoxicillin clavulanate dispensing please login to “mybpac” at www.bpac.org.nz
- Health Protection Agency (HPA) and Association of Medical Microbiologists. Management of infection guidance for
primary care for consultation and local adaptation. HPA, 2013. Available from:
www.hpa.org.uk (accessed Jul, 2013)
- bpacnz. Antibiotics, choices for common infections , 2013. Available from www.bpac.org.nz (accessed Jul, 2013)